Osteoporosis

What is Osteoporosis?
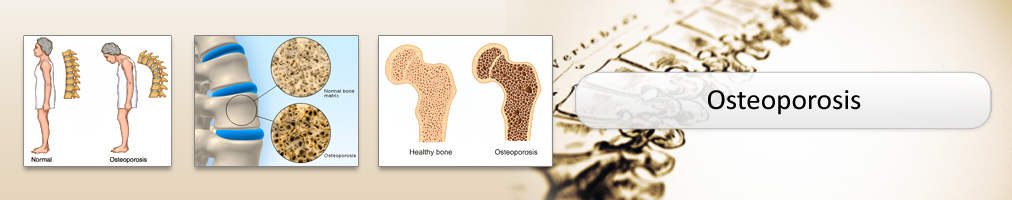
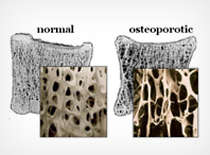
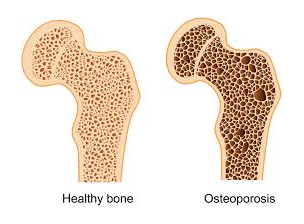
a systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to enhanced bone fragility and a consequent increase in fracture risk.

Osteoporosis Symptoms:
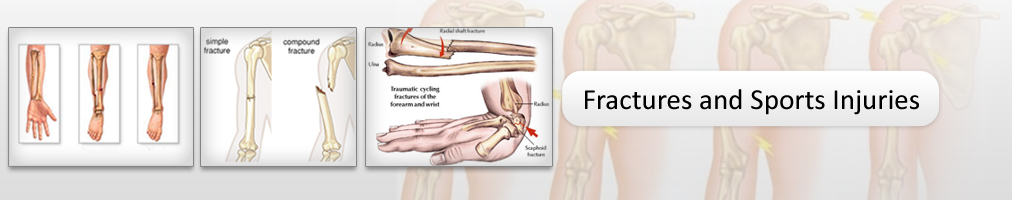
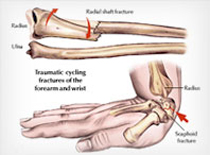
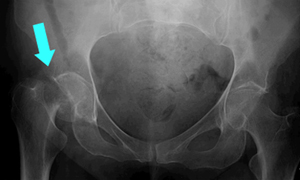
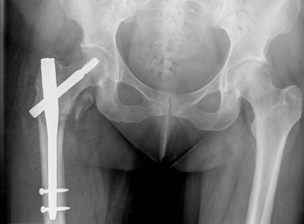
- Mostly asymptomatic until fracture- A person with osteoporosis can fracture a bone from a minor fall, or in serious cases, from a simple action such as a sneeze or even spontaneously.
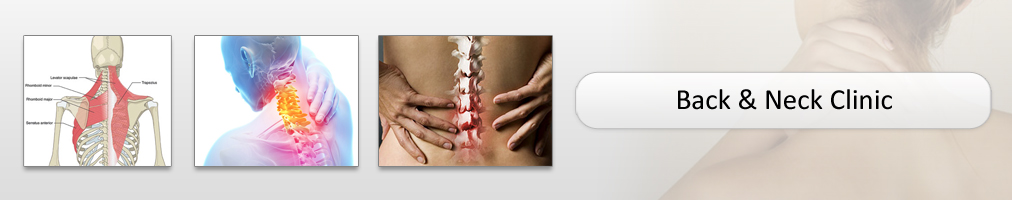
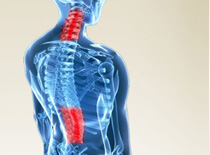
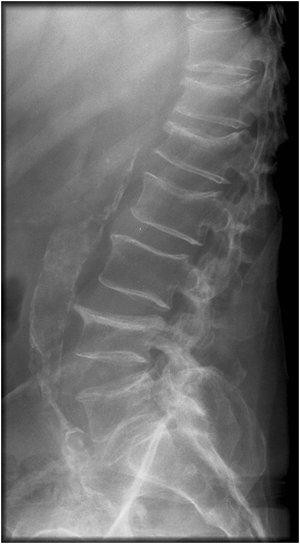
- Vertebral (spinal) fractures may initially be felt or seen in the form of severe back pain, loss of height, or spinal deformities such as kyphosis or stooped posture. In many cases, a vertebral fracture can even occur with no pain.
- Women can lose up to 20 percent of their bone mass in the five to seven years after menopause, making them more susceptible to osteoporosis.

Osteoporosis diagnosis:
Areal bone mineral density is a important predictor of fracture risk.Spine/hip dual energy X-ray absorptiometry measurement (DXA) is the diagnostic standard

When to perform a bone density test National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) Guidelines:
Areal bone mineral density is a important predictor of fracture risk.Spine/hip dual energy X-ray absorptiometry measurement (DXA) is the diagnostic standard
- All postmenopausal women under age 65 who have one or more additional risk factors for osteoporotic fracture (besides menopause)
- All woman aged 65 and older regardless of additional risk factors
- Postmenopausal women who present with fractures
- If BMD would facilitate decision of whether or not to start treatment